医科学専攻
- Master's Courses
修士課程 - Doctoral Courses
博士課程
Modomics Biology and Medicine(Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer)モドミクス医学(加齢医学研究所)
STAFF
Professor
-
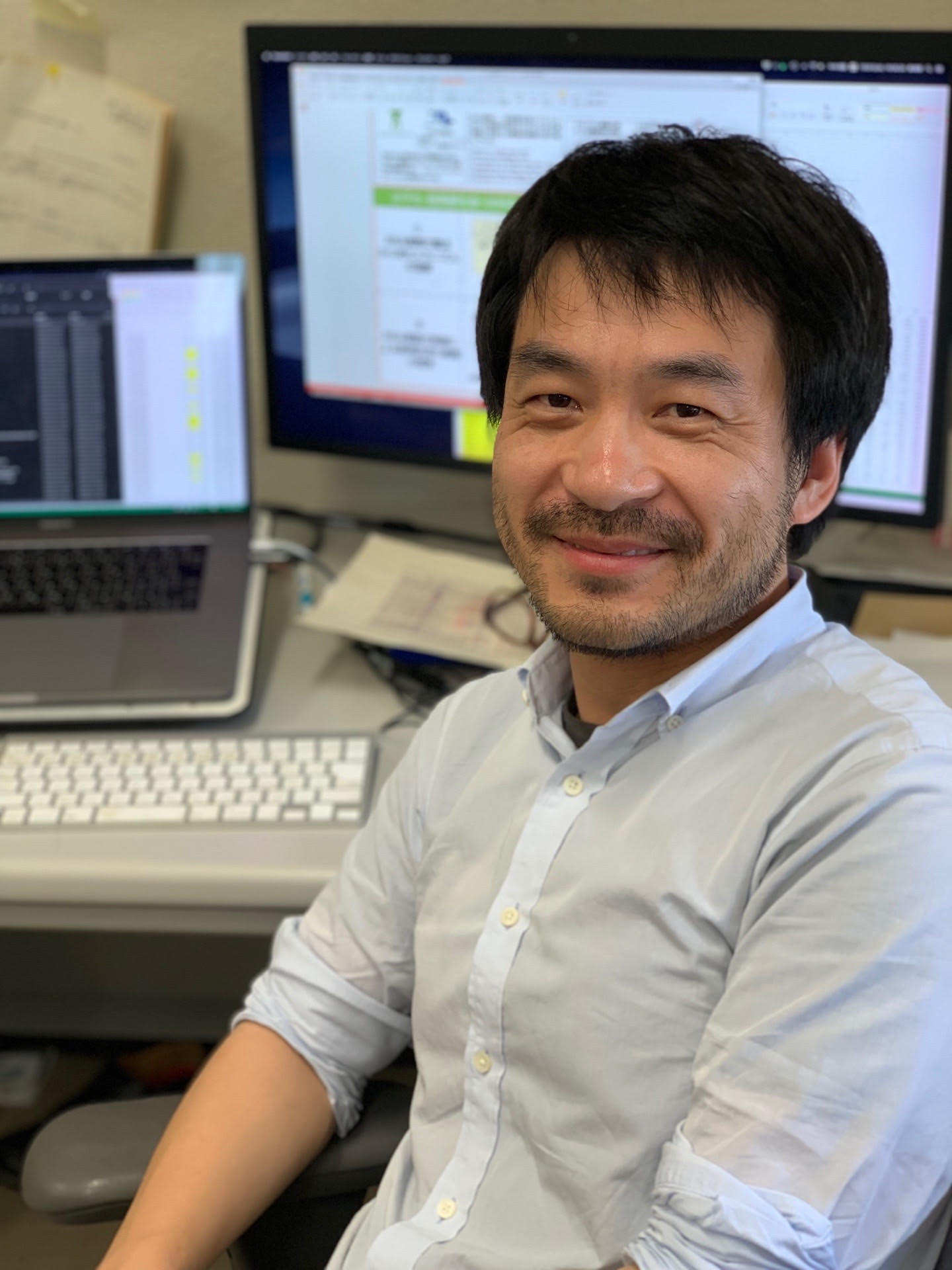
Wei Fan YanProfessor. 魏 范研 教授

Other Faculty / Staff
-
Ogawa, Akiko
Assistant Prof. 小川 亜希子 助教 -
Matsuda, Shigeru
Assistant Prof. 松田 盛 助教
CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-717-8569
E-MAIL:fanayan.wei.d3*tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
More than 150 types of post-transcriptional modifications have been identified in various RNA species, including messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA), from all three domains of life. These modifications are vital for RNA stability, intracellular localization, and decoding fidelity. Dysregulated modification of RNA has been associated with various human diseases, such as diabetes, mitochondrial disease, and intellecutual disability. In addition to regulating intracellular post-transcriptional gene expression, RNA modifications can greatly impact extracellular signaling because modified RNAs are catabolized into modified nucleosides that are released into extracellular fluids. These extracellular modified nucleosides are not only utilized as potential biomarkers of diseases, but also can act as ligands of selective receptors and trigger pathophysiological responses. Our labolatory investigates the molecular mechanism of regulatory roles of RNA modification both intracellularly and extracellulary.
外界からの化学的・物理的・生物学的なストレス、あるいは疾患や加齢などの内的要因によって、我々の体の中では様々な生体分子がダイナミックに「化学修飾」を受けることで新たな機能を獲得し、細胞や臓器機能に影響を及ぼしています。
これらの修飾の網羅的な解析を「モドミクス(Modification + Omics)」と名付け、私たちは中でも特にRNA修飾に注目し、RNAモドミクスと代謝・免疫・老化などの生理機能やヒト疾患病態との関わりについて先進的な研究を行っています。

Mass Spec
質量分析装置
Cell culture
細胞培養
Microscope
顕微鏡
ARTICLE
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an endogenous A3 adenosine receptor ligand.
Ogawa A, Nagiri C, Shihoya W, Inoue A, Kawakami K, Hiratsuka S, Aoki J, Ito Y, Suzuki T, Suzuki T, Inoue T, Nureki O, Tanihara H, Tomizawa K, Wei FY.
Mol Cell. 81(4):659-674.e7. 2021.
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33472058/
Loss of Ftsj1 perturbs codon-specific translation efficiency in the brain and is associated with X-linked intellectual disability.
Nagayoshi Y, Chujo T, Hirata S, Nakatsuka H, Chen CW, Takakura M, Miyauchi K, Ikeuchi Y, Carlyle BC, Kitchen RR, Suzuki T, Katsuoka F, Yamamoto M, Goto Y, Tanaka M, Natsume K, Nairn AC, Suzuki T, Tomizawa K, Wei FY.
Sci Adv. 7(13):eabf3072. 2021
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33771871/
Ogawa A and Wei FY.
Protocol for preparation and measurement of intracellular and extracellular modified RNA using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
STAR Protoc. in press. 2021
Cdk5rap1-mediated 2-methylthio modification of mitochondrial tRNAs governs protein translation and contributes to myopathy in mice and humans.
Wei FY, Zhou B, Suzuki T, Miyata K, Ujihara Y, Horiguchi H, Takahashi N, Xie P, Michiue H, Fujimura A, Kaitsuka T, Matsui H, Koga Y, Mohri S, Suzuki T, Oike Y, Tomizawa K.
Cell Metab. 21(3):428-42. 2015
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25738458/
Deficit of tRNA(Lys) modification by Cdkal1 causes the development of type 2 diabetes in mice.
Wei FY, Suzuki T, Watanabe S, Kimura S, Kaitsuka T, Fujimura A, Matsui H, Atta M, Michiue H, Fontecave M, Yamagata K, Suzuki T, Tomizawa K.
J Clin Invest. 121(9):3598-608. 2011
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21841312/
 2025年度 医学部奨学賞・東北医学会奨学賞・医学部学生奨学賞授与式を行いました
2025年度 医学部奨学賞・東北医学会奨学賞・医学部学生奨学賞授与式を行いました
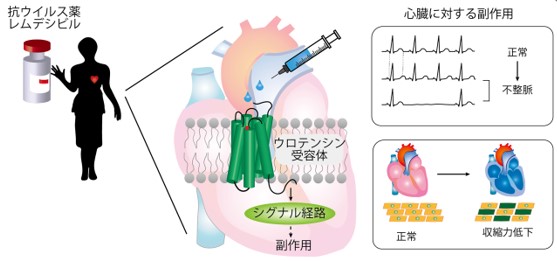 COVID-19治療薬の副作用の仕組みを解明 -受容体経路を抑制することで副作用改善の可能性-
COVID-19治療薬の副作用の仕組みを解明 -受容体経路を抑制することで副作用改善の可能性-