医科学専攻
- Master's Courses
修士課程
Biomedical Imaging(Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering)医用イメージング研究(医工学研究科)
STAFF
Professor
-
SAIJO, YoshifumiProfessor. 西條 芳文 教授

CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-717-8514
E-MAIL:saijo*idac.tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
Our laboratory is studying novel signal and image processing methods of ultrasound, CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) in order to realize 3D imaging, precise automatic diagnosis and cardiovascular blood flow analysis. Besides analysis of conventional medical imaging modalities, we are investigating biomechanics of biological tissues such as atherosclerosis, heart, tendon, cartilage, bone, tooth and living cell by our originally developed ultrasound microscopes. Photoacoustic (PA) effect is a phenomenon in which ultrasound is generated by thermal expansion of the tissue by nano-second pulsed laser irradiation. We have recently started a big research project on real time high resolution PA imaging for visualization of vasculature of small vessels and slow blood flow that is not detectable by conventional ultrasound Doppler technique.
We have been interested in multimodality blood flow imaging of cardiovascular system. 2D blood flow vector was obtained by Echodynamography in which some fluid dynamics theories are applied to conventional color Doppler data set and by two-directional observation of the blood flow by very high frame rate ultrasound imaging. These methods are confirmed by particle image velocimetry of phantom flow in lucent carotid artery model based on 3D CT data.
私たちの研究室では、超音波、CT(コンピュータ断層法)、MRI(磁気共鳴画像)などの臨床データを基に、心臓や血管などの三次元イメージングや自動組織診断、心血管系の血流の流体力学的解析などを行っています。また、既存の診断モダリティーの解析だけではなく、医学・生物学用超音波顕微鏡や光音響顕微鏡などの新しいデバイスを開発し、動脈硬化、心臓、腱、軟骨、骨、歯などの組織や生きた細胞のバイオメカニクス計測に応用しています。光音響効果はナノ秒パルスレーザーの照射により局所的に熱膨張した組織が超音波を発生する現象です。2014年からは、従来の超音波ドプラ法では検出できない細い血管の遅い血流を可視化するリアルタイム高解像度光音響イメージングの開発に着手しています。
種々のモダリティーを応用した心血管系の血流解析は継続して研究しており、カラードプラ心エコーデータに流体力学の諸法則を適用して2次元血流を得るエコーダイナモグラフィーや非常に速いフレームレートで2方向から血流を観察する手法で、2次元血流ベクトルを得ることに成功しています。現在、流れの可視化方法が確立され、3次元CTデータを基に作製した透明の頸動脈モデル内の流れの解析により、これらの手法の検証を行っています。
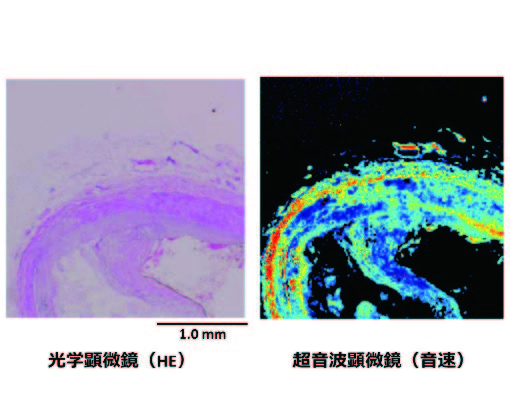
Figure 1. Imaging of vulnerable plaque with optical and ultrasound microscopy
Figure 1 不安定プラークの光学・超音波顕微鏡像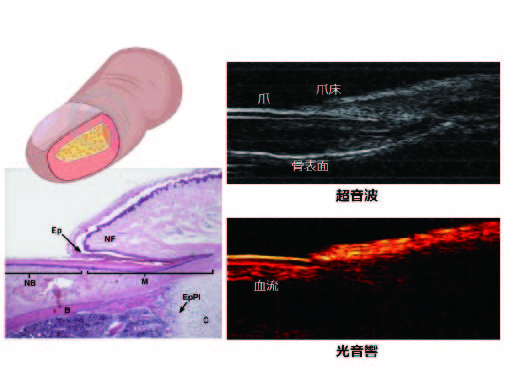
Figure 2. Imaging of finger with ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
Figure 2 指先の超音波・光音響イメージング
ARTICLE
Patient hiPSCs Identify Vascular Smooth Muscle Arylacetamide Deacetylase as Protective against Atherosclerosis.
Gut microbiome-derived phenyl sulfate contributes to albuminuria in diabetic kidney disease.
Nagaoka R et al. Ultrasonic measurement of microdisplacement induced by acoustic radiation force. Jpn J Appl Phys. 52(7S), 07HF21, 2013.
Mitochonic acid MA-5 binds to mitochondria and ameliorates renal tubular and cardiac myocyte damages.
Alteration of the intestinal environment by lubiprostone is associated with amelioration of adenine-induced CKD.
Conformational change in tRNA is an early indicator of acute cellular damage with prognostic significance.

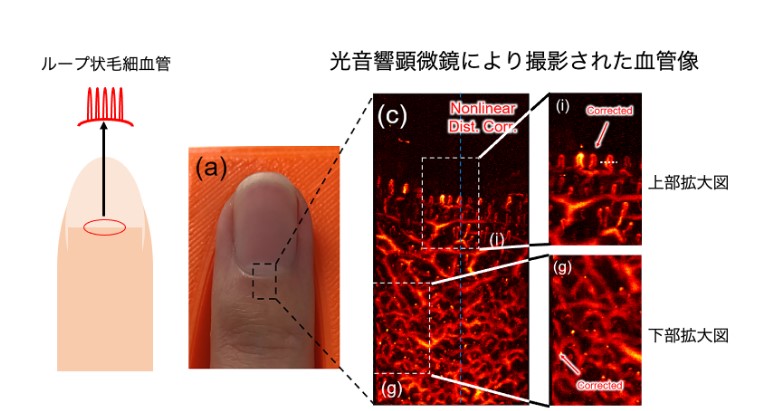 限界を突破し皮下のループ状毛細血管を世界で初めて可視化 光音響顕微鏡の高精度制御により高画質を実現
限界を突破し皮下のループ状毛細血管を世界で初めて可視化 光音響顕微鏡の高精度制御により高画質を実現