医科学専攻
- Doctoral Courses
博士課程
Department of Diabetes, Metabolism and Endocrinology糖尿病代謝・内分泌内科学
STAFF
Professor
-
Katagiri, HidekiProfessor. 片桐 秀樹 教授

Other Faculty / Staff
-
Imai, Junta
Assoc. Prof. 今井 淳太 准教授 -
Takahashi, Kei
Assistant Prof. 高橋 圭 助教
CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-717-7611
E-MAIL:hisyodme*grp.tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
Our department is dedicated to conducting research aimed at developing therapeutic and preventive strategies against metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. To achieve these goals, we have been elucidating the mechanisms that maintain homeostasis of glucose and energy metabolism in multi-organ organisms.
1) Inter-Organ Neuronal Communication and Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration
We have discovered and profounded the importance of inter-organ networks via the nervous system (Science 2006, 2008, Cell Metab 2006, 2012, Nat Commun 2015, 2017, 2018, 2023, Nat Biomed Eng 2024 etc.). By elucidating these molecular mechanisms, we aim to develop new regenerative medicine strategies for the cure of diabetes by increasing the patient’s own β cells at sites where they should be.
2) The Roles of the Liver in Metabolic Homeostasis at the Whole-body Level
Our research is also focused on the roles of the liver in metabolic homeostasis at the whole-body level (Cell Rep 2023, Nat Metab accepted, etc). While fasting, the liver releases glucose with neither excess nor deficiency through glycogenolysis and glycogenesis. After a meal, the liver is the first organ to receive nutrients and insulin from the portal vein. Disturbance of this precise mechanism leads to metabolic diseases. Therefore, we aim to clarify these roles of the liver and develop new strategies to prevent/treat diabetes.
Through the Moonshot Research Project, of which Professor Katagiri is the project manager, we are promoting research on the eradication of metabolic diseases in collaboration with many researchers in a broad range of fields.
当分野では、糖尿病や肥満などの代謝疾患に対する治療・予防法の開発に向けた研究を進めています。そのために、多臓器生物が糖代謝やエネルギー代謝の恒常性を維持するメカニズムの解明を進め、その機構として、神経系を介した臓器間ネットワークを発見しその重要性を提唱してきました(Science 2006, 2008, Cell Metab 2006, 2012, Nat Commun 2015, 2017, 2018, 2023, Nat Biomed Eng 2024 など)。これらの分子機構を解明することで、体内で自分のβ細胞を増やすことで糖尿病を治療する全く新しい再生医療の開発を目指しています。
さらに最近は、全身の代謝恒常性における肝臓の役割についても注目をして研究を進めています(Cell Rep 2023, Nat Metab acceptedなど)。肝臓は、食後の糖を最初に処理する臓器であり、空腹時は過不足なくブドウ糖を放出しています。この精密な仕組みの乱れが糖尿病などの代謝疾患につながるものと考えられます。そこで、その肝からのメカニズムを明らかとし、糖尿病を予防・治療する新たな手法の開発につなげたいと考えています。
片桐教授がプロジェクトマネージャーを務めるムーンショット研究を通じ、全国の様々な領域の研究者と連携して、代謝疾患の撲滅に向けた研究を推進しています。

Lab Members
教室メンバー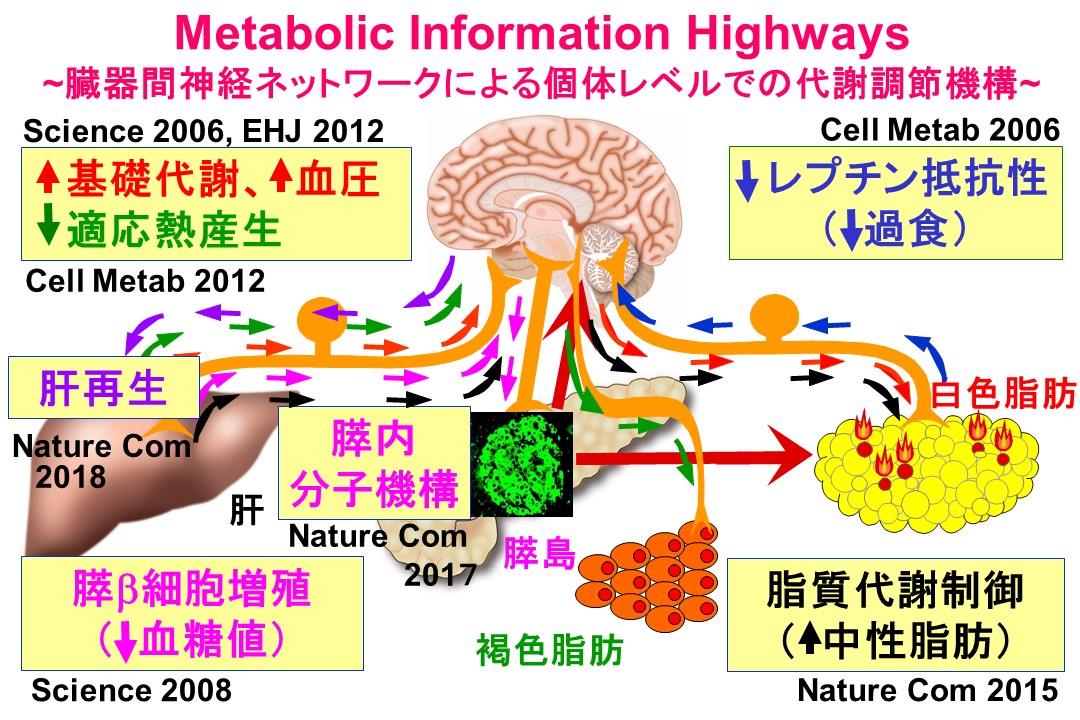
Inter-organ communications via neural systems that we have identified
我々がこれまでに明らかとした臓器間神経ネットワーク
ARTICLE
Horiuchi T, et al. Redox-dependent liver gluconeogenesis impacts different intensity exercise in mice. Nature Metabolism accepted
Kawana Y, et al. Optogenetic stimulation of vagal nerves for enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and β cell proliferation. Nature Biomedical Engineering. 8(7):808-822, 2024
Endo A, et al. Phagocytosis by macrophages promotes pancreatic β cell mass reduction after parturition in mice. Developmental Cell. 58(19): 1819-1829, 2023
Sugawara H., et al. A highly sensitive strategy for monitoring real-time proliferation of targeted cell types in vivo. Nature Communications. 14(1): 3253, 2023
Takahashi K, et al. Inter-organ insulin-leptin signal crosstalk from the liver enhances survival during food shortages. Cell Reports. 42(5) 112415, 2023
 2025年度 医学部奨学賞・東北医学会奨学賞・医学部学生奨学賞授与式を行いました
2025年度 医学部奨学賞・東北医学会奨学賞・医学部学生奨学賞授与式を行いました
 糖尿病代謝・内分泌内科学分野の片桐 秀樹教授、今井 淳太准教授が第62回「ベルツ賞」の1等賞を受賞しました
糖尿病代謝・内分泌内科学分野の片桐 秀樹教授、今井 淳太准教授が第62回「ベルツ賞」の1等賞を受賞しました
 肝臓の糖新生が運動能を決める!‐新たな運動持久力向上法、肥満・サルコペニア対処法へ‐
肝臓の糖新生が運動能を決める!‐新たな運動持久力向上法、肥満・サルコペニア対処法へ‐
 糖尿病代謝・内分泌内科学分野の片桐 秀樹教授が2025年度「武田医学賞」を受賞しました
糖尿病代謝・内分泌内科学分野の片桐 秀樹教授が2025年度「武田医学賞」を受賞しました