その他
Autopsy Imaging Centerオートプシー・イメージングセンター
STAFF
Professor
-
Kaneta, TomohiroProfessor. 金田 朋洋 教授 (兼任)
Other Faculty / Staff
-
Usui, Akihito
Lect. 臼井 章仁 講師
CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-717-7943
E-MAIL:kaiseki*med.tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
In recent years, postmortem radiology using CT scanner, that is to say, “Ai: Autopsy imaging” in Japanese, has become popular within the field of legal medicine. In our institute, more than 1,000 cases were analyzed using the multi-slice CT scanner and the 3D workstation between 2009 and 2014. We have offered a lot of useful information to forensic pathologists on the cause of death (e.g. hypothermic death and drowning death), the location of metal weapon(s) in the body, respiratory infectious disease like tuberculosis and so on. In addition, we have carried out many studies on forensic anthropology, such as sex and age determination using CT images.
当センターは法医学および画像解析学の連携により、2009年5月から法医解剖前CT検査を開始し、2022年3月末までに約2,200件の事例について死後画像の撮影、およびその読影を行っています。この中には検案といって、医師が外表検査のみで推定死因を判断するにとどまる例も約200件含まれています。このことは、これらに関しては、解剖せずとも死後CT画像の助けで死因の絞り込みができたということです(もちろん警察による事前の捜査で犯罪性がない、というのが判っていることが前提です)。 法医学実務において放射線を利用した診断技術の確立はそう新しいことではありません。ヴィルヘルム・レントゲンによりX線が発見された19世紀末、すでに銃弾の写真が殺人未遂事件の法廷おいて証拠となったという記録があります。その後、欧米では死者へのX線撮影・診断に関し、”forensic radiology”という学問体系が発展して行きます。しかしわが国では、X線の発明から100年以上が経過しても、法医学教室で独自のレントゲン装置を装備している施設はほとんどありませんでした。それが21世紀に入り、人口あたりのCTの設置台数が世界最多というわが国において、先進国の中でも著しく低い解剖率を補完する目的で、CTを使用した死因究明活動が瞬く間に普及してきました。21世紀初頭といえば作家で医師の海堂尊氏が、その処女作で放射線画像が事件の謎解きの鍵になるミステリー小説を世に出し、大いに話題となった頃ですが、このセンターの名前の由来である「オートプシーイメージング:Ai」という名称は海堂氏が命名したと言われています。 われわれのAiセンターでは、単に死後CT画像の撮影・読影にとどまらず、画像診断の新たな展開を目指しての研究を鋭意行っており、これまでにも低体温症(凍死)に特徴的な画像所見や、溺死体の副鼻腔や肺にみられるパターンの分析、あるいは甲状軟骨や肋骨のCT画像を用いた年齢推定法などについても論文発表を行っています。なお、これらをまとめたものが成書として出版されており、死後CT撮影でお悩みの医療関係者の方は参照ください(舟山眞人・齋藤春夫監修. Aiはどこまで事実に迫るか.医歯薬出版.2014)。
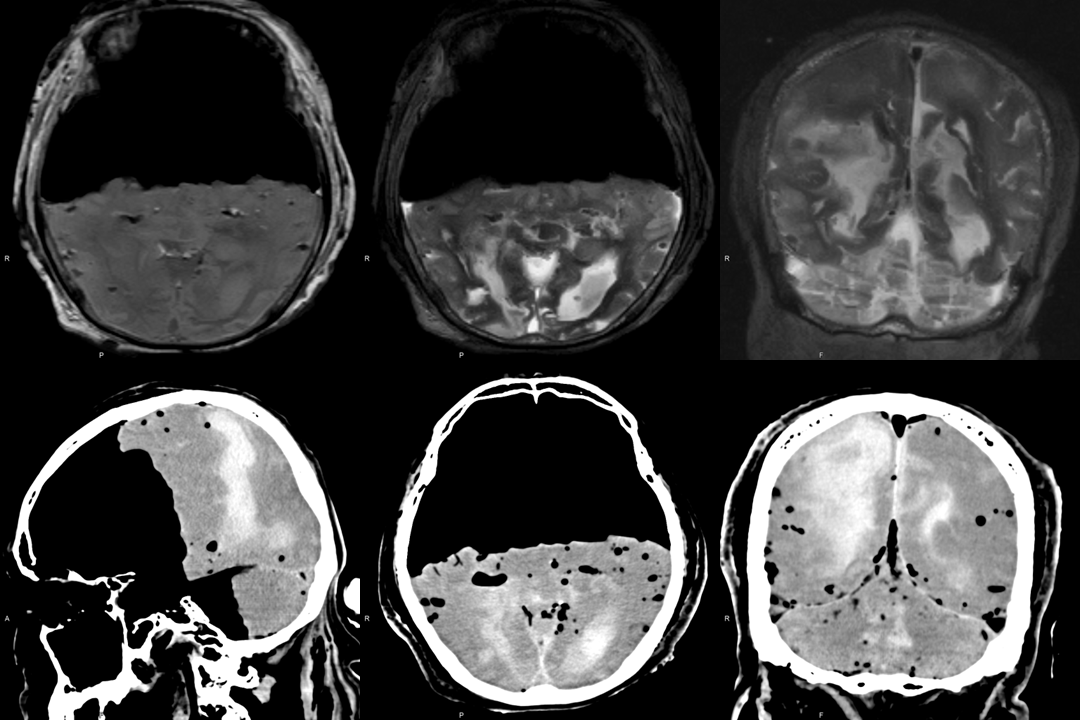
Intracerebral hemorrhage in a highly decomposed body
高度腐敗症例における脳内出血
ARTICLE
Zeng Y, et al. Deep Learning-Based Diagnosis of Fatal Hypothermia Using Post-Mortem Computed Tomography. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2023;260:253-261.
Zeng Y, et al. A 2.5D Deep Learning-Based Method for Drowning Diagnosis Using Post-Mortem Computed Tomography. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023;27:1026-1035.
Ogawara T, Usui A, Homma N, Funayama M. Diagnosing Drowning in Postmortem CT Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022;259:65-75.
Okumura S, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Liver Damage Based on Postmortem Computed Tomography Findings in High-Energy Trauma. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022;257:327-332.
Kudo S, et al. Cervical intervertebral separation caused by trauma on post-mortem computed tomography: Possibility of a diagnosis based on intervertebral gas. Forensic Sci Int. 2022;330:111049.
