医科学専攻
- Master's Courses
修士課程 - Doctoral Courses
博士課程
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology(Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization)分子医化学(東北メディカル・メガバンク 機構)
STAFF
Professor
-
Yamamoto, MasayukiProfessor. 山本 雅之 教授

Other Faculty / Staff
-
Suzuki, Takafumi
Assoc.Prof. 鈴木 隆史 准教授 -
Ikehata, Hironobu
Assoc.Prof. 池畑 広伸 准教授 -
Otsuki, Akihito
Lect. 大槻 晃史 講師 -
Liam, Baird
Assistant Prof. Liam, Baird 助教 -
Hidaka, Takanori
Assistant Prof. 日高 高徳 助教 -
Kurosawa, Ryo
Assistant Prof. 黒澤 亮 助教
CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-728-3037
E-MAIL:masayuki.yamamoto.c7*tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
Oxidative stress plays an important role in the initiation and progression of many chronic diseases, including diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Through the regulation of cytoprotective gene expression, the KEAP1-NRF2 stress response pathway is the principal inducible defense against oxidative and electrophilic stresses. Under non-stressed conditions, the transcription factor NRF2 is targeted for ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation by its negative regulator KEAP1, which forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase with CUL3 and RBX1. In response to a wide range of cellular stresses, the KEAP1-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase is inactivated, which results in the stabilization of NRF2, and the upregulation of the antioxidant and cytoprotective gene expression programs. Mammalian models of medically important diseases utilizing Nrf2 knockout (KO) mice have directly implicated NRF2 activity in a wide range of human pathologies, including metabolic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, rheumatoid arthritis, and Alzheimer’s disease. The inducible nature of the pathway means that, by clearly delineating the molecular mechanism of NRF2 activation, we can optimize the design and activity of NRF2 modulators in order to mitigate the deleterious effects of oxidative stress on human health. As such, a thorough understanding of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway may lead to the development of novel treatments for a broad range of human diseases.
活性酸素種や食物に含まれる親電子性物質などの酸化ストレスは、DNAやタンパク質、脂質などの生体高分子を酸化することで傷害を与えるため、がんや糖尿病などの生活習慣病を引き起こす素因になると考えられています。このような酸化ストレスに対し、細胞はすみやかに生体応答を発動することで、その恒常性維持と適応に努めています。この生体応答の制御機構において、重要な機能を担っているのが、Keap1-Nrf2システムです。Keap1-Nrf2システムの活性化は、糖尿病やアルツハイマー病など様々な疾患に改善効果をもたらし、Nrf2活性化剤がこれらの疾患の新たな治療薬として期待されています。また、Nrf2は、微小重力や宇宙放射線からのストレス防御にも貢献していることが、最近の私たちの研究から明らかとなりました。分子医化学分野では、ゲノム編集技術等を用いて独自の遺伝子改変マウスを作製し、解析を行っています。構造生物学的なアプローチも取り入れ、多角的にKeap1-Nrf2システムによる分子レベルの制御機構とその生理機能を解明し、世界をリードし続けています。
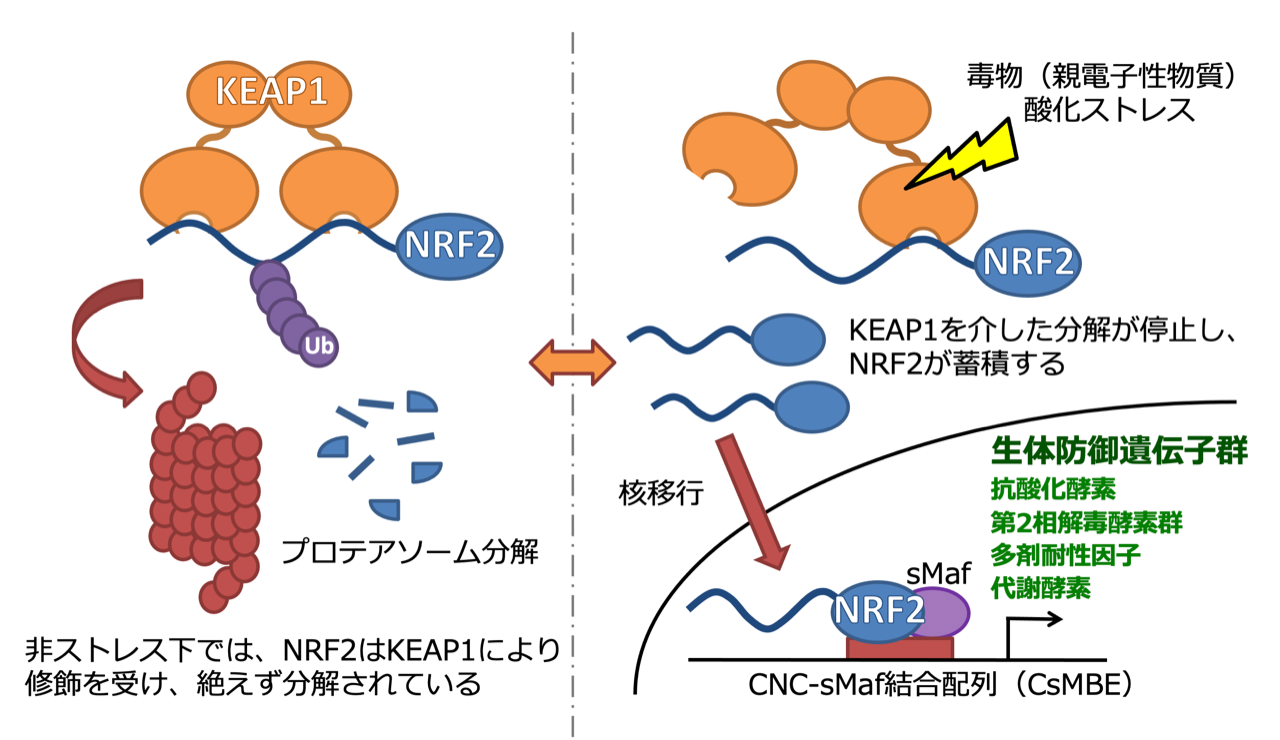
Keap1-Nrf2 system
Keap1-Nrf2システム
Histological analysis
組織学的解析
Genome editing in mice
ゲノム編集マウス作製
ARTICLE
Yamamoto M, et al. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: a Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 98(3):1169-1203, 2018
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29717933/
Suzuki T, et al. Environmental pollutants and the immune response. Nature Immunol 21(12):1486-1495, 2020
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33046888/
Suzuki T, et al. Nrf2 contributes to the weight gain of mice during space travel. Commun Biol 3(1):496, 2020
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32901092/
Horie Y, et al. Molecular basis for the disruption of Keap1-Nrf2 interaction via Hinge & Latch mechanism. Commun Biol 4(1):576, 2021
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33990683/
Hirose W, et al. Selective Elimination of NRF2-Activated Cells by Competition with Neighboring Cells in the Esophageal Epithelium. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15(1): 153-178, 2023
URL:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36115578/
 2025年度 辛酉優秀学生賞授与式を行いました
2025年度 辛酉優秀学生賞授与式を行いました
 食道扁平上皮がんにおいて生体防御遺伝子が高頻度に変異する原因を解明
食道扁平上皮がんにおいて生体防御遺伝子が高頻度に変異する原因を解明
 令和5年度 辛酉優秀学生賞授与式が行われました
令和5年度 辛酉優秀学生賞授与式が行われました