医科学専攻
- Master's Courses
修士課程 - Doctoral Courses
博士課程
AI and Innovative Medicine(United Centers for Advanced Research and Translational Medicine)AIフロンティア新医療創生(附属創生応用医学研究センター)
STAFF
Professor
-
Tamiya, GenProfessor.Ph.D. 田宮 元 教授

Other Faculty / Staff
-
Takayama, Jun
Assoc. Prof.Ph.D. 高山 順 准教授 -
Shirota, Matsuyuki
Lect.M.D. Ph.D. 城田 松之 講師 -
Kyosaka, Tomoki
Res Fellow.M.D. Ph.D. 京坂 朋来 学術研究員
CONTACT
TEL:+81-22-728-3071
E-MAIL:info*mai.med.tohoku.ac.jp
(「*」を「@」に変換してください)
OUTLINE
Our research aims to contribute to sustainable medicine by identifying the genome variations, lifestyles, and interactions that underlie common diseases and health conditions by applying state-of-the-art mathematical methods, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies, to medical big data such as genome cohort/biobanks.
Our main research themes include identifying disease- or trait-related genes, lifestyles, and their interactions using large-scale genome cohort/biobank data. These data are used to estimate the risk of disease onset, implement genomic health screening, and deploy in precision medicine. We apply AI technologies to the differential diagnosis of rare diseases and cancer with clinical sequencing data. In addition, we utilize electronic medical record information via large language models.
Our laboratory closely coordinates with the Department of Statistical Genomics and Genetics in Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization and Statistical Genetics Team of RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligent Project, where Tamiya is the team leader. By making full use of one of the world's leading supercomputers in life sciences and the world's largest AI supercomputer, we can research at a scale and accuracy that other facilities unmatch. We are also actively engaged in application-oriented joint research with pharmaceutical and information companies.
AIフロンティア新医療創生分野では、ゲノムコホート・バイオバンクのようなビッグデータから、人工知能(AI)・機械学習技術を含む最先端の数理解析手法を用いて、疾患や健康状態の背景となるゲノムや生活習慣、その相互作用を同定し、持続可能な医療に資することを目的とした研究を行っています。 主な研究テーマは、大規模ゲノムコホート・バイオバンクデータを用いた疾患・形質関連遺伝子や生活習慣、その相互作用の同定と、それを用いた疾患発症リスク推定、ゲノム検診への実装と精密医療への展開などがあります。また、希少難病・がんクリニカルシークエンス解析やその鑑別診断への人工知能技術の応用、大規模言語モデル・生成AI技術による電子カルテ情報の利活用も行っています。 また、東北メディカル・メガバンク機構協力講座であるゲノム遺伝統計学分野や、田宮がチームリーダーを努める理化学研究所革新知能統合研究センター・遺伝統計学チームと密接に連携しています。生命科学分野では世界でも有数のスーパーコンピュータや人工知能解析に特化した世界最大のAIスーパーコンピュータを駆使して、他の施設ではなしえない規模と精度での研究が可能になっています。製薬企業・情報系企業との応用志向の共同研究も活発に行われています。
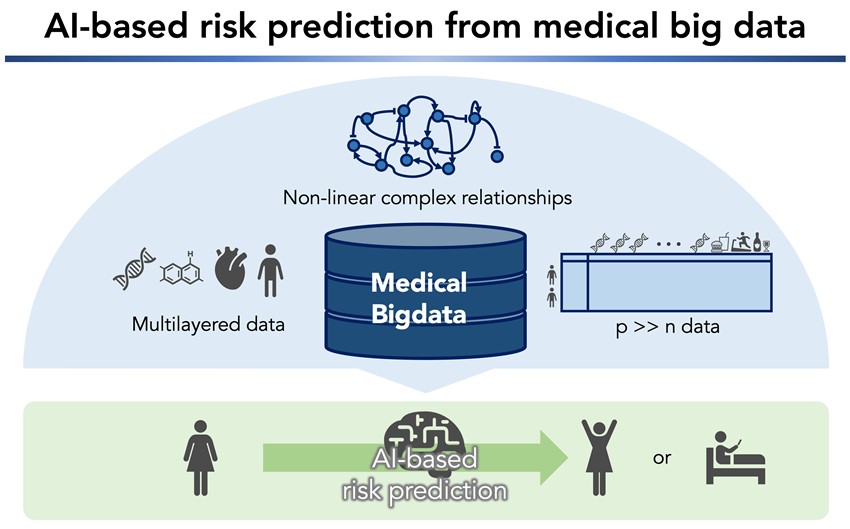
AI-based risk prediction from medical big data
AIによる医用ビッグデータからのリスク予測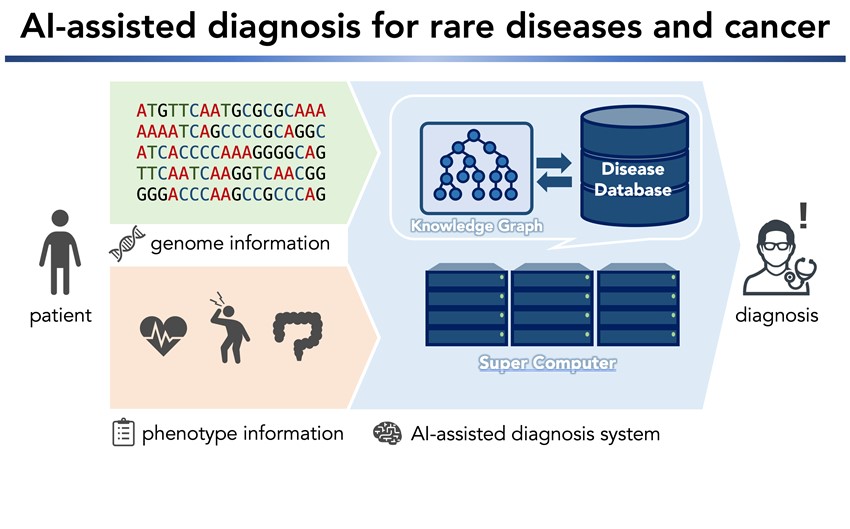
AI-assisted diagnosis for rare diseases and cancer
AIによる希少難病やがんの診断支援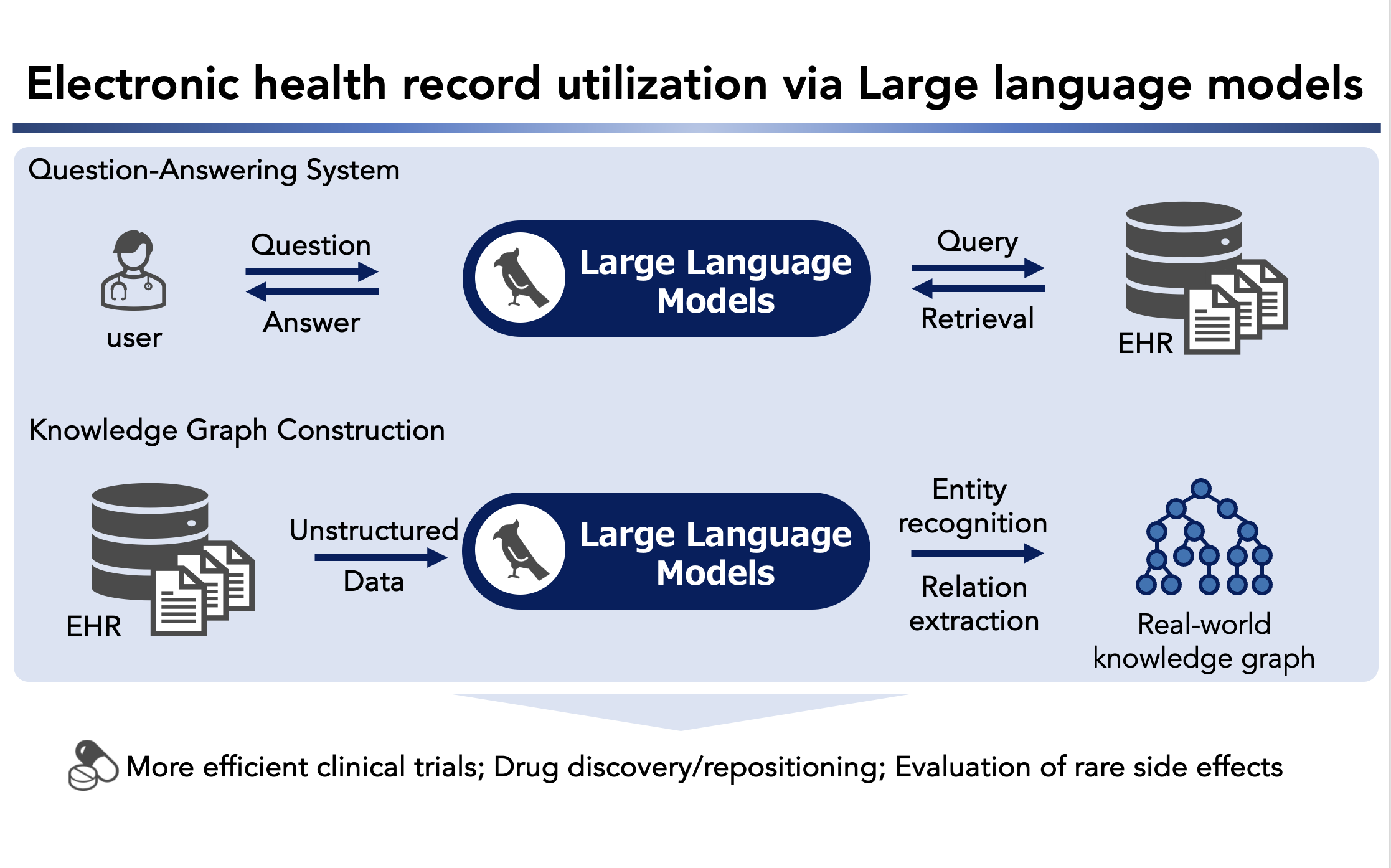
Utilization of electronic health records with large language models
大規模言語モデルを用いた電子カルテデータの利活用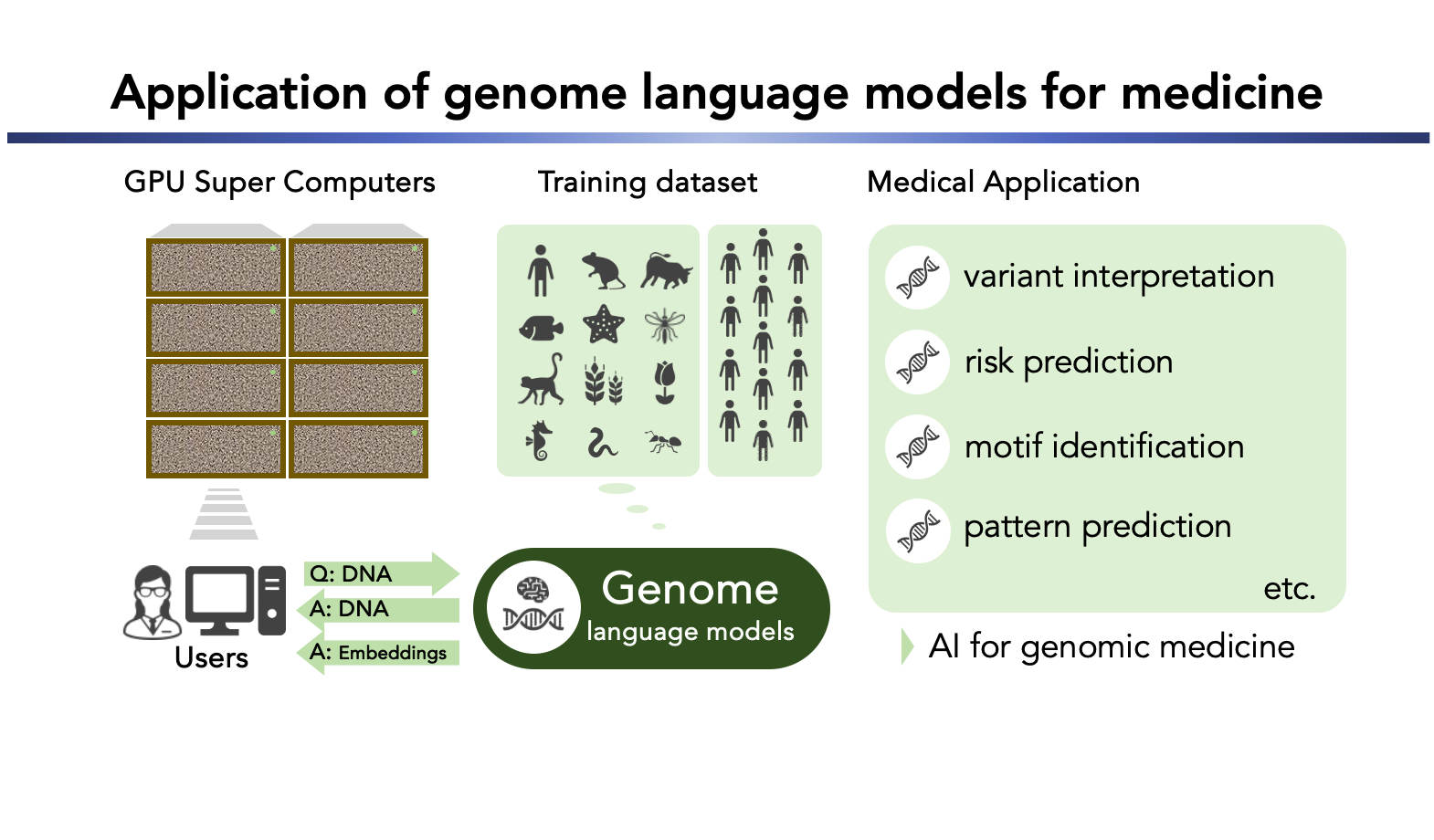
Applying genome language models to medicine
医療に活かすゲノム言語モデル
ARTICLE
Hatzikotoulas K, et al. Translational genomics of osteoarthritis in 1,962,069 individuals.
Nature. 641(8065):1217-1224, 2025
URL:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08771-z
Ojima T, et al. Body mass index stratification optimizes polygenic prediction of type 2 diabetes in cross-biobank analyses.
Nature Genetics. 56(6):1100-1109, 2024
URL:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-024-01782-y
Graham SE, et al. The power of genetic diversity in genome-wide association studies of lipids.
Nature. 600(7890):675-679, 2021
URL:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04064-3
Takayama J, et al. Construction and integration of three de novo Japanese human genome assemblies toward a population-specific reference.
Nature Communications. 12(1):226, 2021
URL:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20146-8
Yamamoto Y, et al. Automated acquisition of explainable knowledge from unannotated histopathology images.
Nature Communications. 10(1):5642, 2019
URL:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-13647-8

 呼吸器・免疫疾患と心血管代謝疾患の遺伝的背景の多様性を解析 〜東アジア系集団と欧州系集団では、両疾患が逆方向の遺伝的相関を示す~
呼吸器・免疫疾患と心血管代謝疾患の遺伝的背景の多様性を解析 〜東アジア系集団と欧州系集団では、両疾患が逆方向の遺伝的相関を示す~
 BMI×ゲノムで2型糖尿病の遺伝的リスク予測精度を向上 〜やせているのに糖尿病になりやすい体質〜
BMI×ゲノムで2型糖尿病の遺伝的リスク予測精度を向上 〜やせているのに糖尿病になりやすい体質〜
 AIフロンティア新医療創生分野の田宮 元教授、高山 順准教授らの論文が国際科学誌Clinical Geneticsに掲載されました
AIフロンティア新医療創生分野の田宮 元教授、高山 順准教授らの論文が国際科学誌Clinical Geneticsに掲載されました
 家族性先天性甲状腺機能低下症を起こすゲノム異常を特定 〜遺伝性疾患研究は新たな段階へ〜
家族性先天性甲状腺機能低下症を起こすゲノム異常を特定 〜遺伝性疾患研究は新たな段階へ〜